This post was also published on Elevate Tech Blog on Medium
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI development, one of the most significant challenges has been the transition from prototype to production. While creating AI agents locally is becoming increasingly accessible, deploying them securely at scale has remained a complex endeavor — until now. Amazon Bedrock AgentCore is changing this paradigm, making production deployment of AI agents straightforward and efficient.
What is Amazon Bedrock AgentCore?
Amazon Bedrock AgentCore, announced recently by AWS, is a fully managed service that enables developers to securely deploy and operate AI agents at scale. It provides a standardized runtime environment for AI agents, handling the infrastructure complexities so developers can focus on agent functionality.
The key benefits of AgentCore include:
- Simplified Deployment: Deploy any AI agent framework with a standardized container interface
- Scalable Infrastructure: Automatically scales to handle varying workloads
- Security and Compliance: Built-in security features and compliance with AWS standards
- Monitoring and Observability: Integrated logging and monitoring capabilities
- Cost Optimization: Pay only for what you use with no upfront costs
AgentCore Architecture Overview
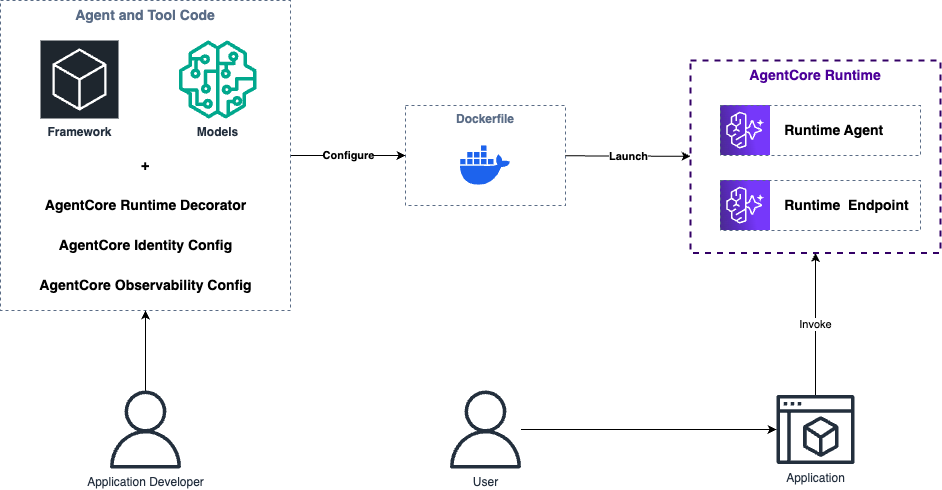
The diagram above illustrates the end-to-end workflow for deploying AI agents with Amazon Bedrock AgentCore:
-
Development Phase: The application developer combines their AI framework (LangChain, LlamaIndex, Strands Agents, etc.) and model of choice with AgentCore-specific components:
- AgentCore Runtime Decorator to standardize the interface
- AgentCore Identity configuration for authentication and permissions
- AgentCore Observability configuration for monitoring and logging
-
Containerization: The agent code is packaged into a Docker container using a Dockerfile, which configures the runtime environment and dependencies.
-
Deployment: AWS launches the containerized agent in the AgentCore Runtime environment, creating:
- A Runtime Agent that executes your AI agent's logic
- A Runtime Endpoint that provides a standardized API for invocation
-
Usage: End users interact with the deployed agent through applications that invoke the AgentCore endpoint.
From Local Development to Production: A Practical Example
To demonstrate how easy it is to deploy an AI agent to production with AgentCore, we'll use a real-world example: the Open Deep Research agent built with LangChain. This agent can perform deep research on topics by breaking them down, searching for information, and synthesizing findings into comprehensive reports.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have:
- uv (Python package manager)
- Docker with buildx plugin
- AWS Account configured with the AWS CLI (you can use a free tier account — new customers can get started with up to $200 in credits as announced here)
Step 1: Clone and Set Up the Repository
First, let's get the code and set up our environment:
git clone https://github.com/sebastianhof/open_deep_research.git
cd open_deep_research
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
Install the required packages:
uv pip install -r pyproject.toml
Copy the environment configuration:
cp .env.example.aws .env
Step 2: Add AgentCore SDK and Create an Entrypoint
Install the Bedrock AgentCore SDK:
uv add bedrock-agentcore
Now, create an entrypoint file that will serve as the interface between AgentCore and our agent. Create a new file at src/agent.py:
from bedrock_agentcore.runtime import BedrockAgentCoreApp
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
from open_deep_research.deep_researcher import deep_researcher_builder
app = BedrockAgentCoreApp()
graph = deep_researcher_builder.compile(checkpointer=MemorySaver())
@app.entrypoint
async def invoke_agent(request, context):
user_msg = request.get("prompt", "No prompt found in input, please guide customer as to what tools can be used")
stream = graph.astream(
{
"messages": [HumanMessage(content=user_msg)]
},
config={
"configurable": {
"thread_id": context.session_id,
}
},
stream_mode="updates"
)
async for update in stream:
if "__end__" not in update:
for node, messages in update.items():
for message in messages:
if isinstance(message, AIMessage) and message.content:
yield {"response": message.content}
This code:
- Creates a BedrockAgentCoreApp instance
- Compiles our deep researcher agent graph
- Defines an entrypoint function that processes incoming requests
- Streams the agent's responses back to the caller
Step 3: Create a Dockerfile
Create a Dockerfile in the root directory:
# Use uv's Python base image
FROM ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:python3.11-bookworm-slim
WORKDIR /app
# Copy all necessary files for the build
COPY pyproject.toml uv.lock README.md ./
COPY src/ src/
COPY tests/ tests/
# Install dependencies (including the local package)
RUN uv sync --frozen --no-cache
# Expose port
EXPOSE 8080
# Run application
CMD ["uv", "run", "uvicorn", "src.agent:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8080"]
Step 4: Build and Push to Amazon ECR
First, set up some environment variables:
export AWS_REGION=<YOUR_AWS_REGION> # e.g., us-east-1, eu-central-1, etc.
export AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query Account --output text)
Create an ECR repository:
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name open-research-agent --region $AWS_REGION
Log into ECR:
aws ecr get-login-password --region $AWS_REGION | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com
Build and push the Docker image:
docker buildx build --platform linux/arm64 -t $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com/open-research-agent:latest --push .
Verify the image was pushed:
aws ecr describe-images --repository-name open-research-agent --region $AWS_REGION
Step 5: Deploy to Amazon Bedrock AgentCore
You have multiple options for deploying your agent to AgentCore:
- AWS Management Console
- AgentCore Starter Toolkit: A CLI tool for streamlined deployments (GitHub Repository)
- AWS CLI: Command-line deployment for automation and scripting (Documentation)
- Boto3 SDK: Programmatic deployment from Python applications (API Reference)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) options such as CloudFormation, CDK, or Terraform are currently not available but will be provided in the future.
For this tutorial, let's walk through the AWS Console approach:
-
Go to the Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Service
-
On the sidebar under Build and Deploy, click on Agent Runtime and then Host Agent
-
Fill out the form:
- Name: open_research_agent
- Description: A deep research agent powered by LangChain and Claude
- Image URI: Enter the URI of your ECR image
- IAM Permissions: Create and use a new service role
Press enter or click to view image in full size
- Click on "Host Agent"
AWS will begin deploying your agent in a Micro VM environment.
Behind the scenes, AgentCore is provisioning the necessary infrastructure, including:
- Creating a dedicated Micro VM instance for your agent
- Setting up networking and security configurations
- Deploying your container image to the VM
- Configuring the runtime environment with your specified variables
- Establishing monitoring and logging integrations
Once deployment is complete (typically within 1-2 minutes), you'll see a confirmation screen similar to the one below:
Press enter or click to view image in full size
Step 6: Invoke and Test Your Deployed Agent
Now that your agent is deployed, you can interact with it using the AWS SDK. Here's a Python script to test it:
import boto3
import json
import uuid
account_id = '<YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>'
region = '<YOUR_AWS_REGION>'
agentcore_id = '<YOUR_AGENTCORE_ID>' # This is the ID of your deployed agent
client = boto3.client('bedrock-agentcore', region_name=region)
session_id = f'user-session-{uuid.uuid4().hex}'
try:
while True:
prompt = input("Enter prompt (CTRL+C to exit): ")
if not prompt.strip():
continue
response = client.invoke_agent_runtime(
agentRuntimeArn=f"arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:{region}:{account_id}:runtime/{agentcore_id}",
qualifier="DEFAULT",
runtimeSessionId=session_id,
payload=json.dumps({"prompt": prompt}).encode()
)
if "text/event-stream" in response.get("contentType", ""):
# Handle streaming response
content = []
for line in response["response"].iter_lines(chunk_size=10):
if line:
# Parse the event stream
# This is a simplified example - production code would need proper event parsing
content.append(line.decode())
print("Response:", "".join(content))
else:
print("Response:", response["response"].read().decode())
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nExiting...")
The output is showing raw JSON. In a production application, you would parse and format this output for a better user experience.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues with your deployed agent, check CloudWatch Logs for detailed error messages. The logs are automatically created when you deploy your agent to AgentCore.
Common issues include:
- Model Availability: Ensure the models specified in your environment variables are available in your deployment region.
- IAM Permissions: Make sure your agent has the necessary permissions to invoke Bedrock models.
Conclusion
Amazon Bedrock AgentCore represents a significant step forward in the AI agent deployment landscape. By abstracting away the complexities of infrastructure management, it allows developers to focus on what matters most: building intelligent, capable agents.
In this article, we've seen how to take an existing LangChain agent from local development to production deployment with minimal changes to the code. The standardized container interface provided by AgentCore makes this process remarkably straightforward, regardless of which agent framework you're using.
As AI agents become increasingly central to business operations, having a reliable, scalable, and secure deployment option like AgentCore will be invaluable. Whether you're building customer service agents, research assistants, or any other type of AI agent, AgentCore provides the infrastructure you need to deploy with confidence.
What's Next: Extending Your Agent with Tool Capabilities
In the next blog post, we'll explore how to supercharge your deployed agents by integrating external tools and services using the Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Gateway. We'll demonstrate how to extend our research agent with Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration capabilities, enabling it to connect to powerful search providers like Tavily for enhanced research capabilities.
This integration will transform our basic research agent into a sophisticated tool that can:
- Access real-time web search results
- Integrate with multiple data sources simultaneously
- Leverage specialized search APIs for domain-specific research
- Maintain secure, authenticated connections to external services
Stay tuned for a deep dive into building truly connected AI agents that can interact with the broader ecosystem of tools and services!
Next steps
To learn more about Amazon Bedrock AgentCore, check out these resources:
- Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Product Page
- Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Documentation
- Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Samples
Happy agent building!